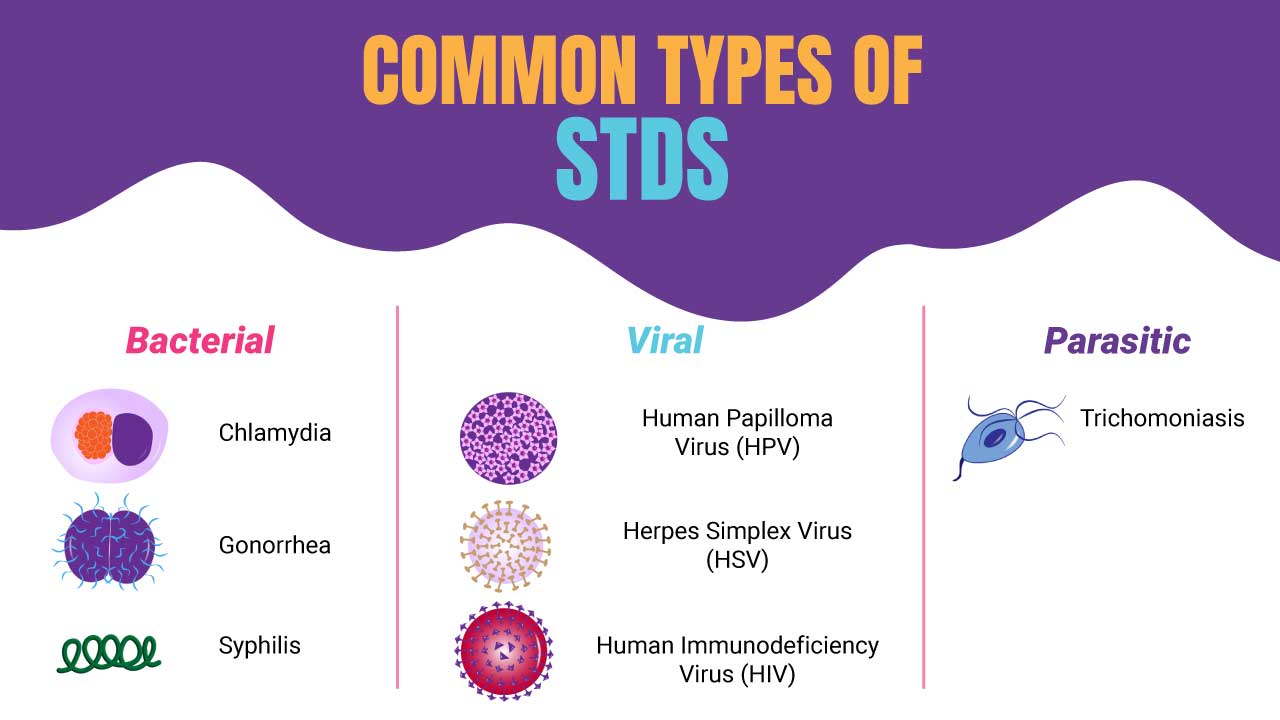
Types of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) come in various forms, each caused by distinct organisms and presenting unique characteristics.
Bacterial STDs
These are caused by bacteria and can often be effectively treated with antibiotics.
- Chlamydia: A very common bacterial sexually transmitted disease (STD) that often shows no symptoms, especially in women. Left untreated, it can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and infertility.
- Gonorrhea: Another common bacterial sexually transmitted disease (STD) that can infect the genitals, rectum, and throat. Symptoms may include burning urination and discharge.
- Syphilis: This bacterial infection if left untreated can potentially leading to serious health problems.
Viral STDs
These are caused by viruses and cannot be cured, but some can be managed with medication to control symptoms and prevent transmission.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): An extremely prevalent virus with different strains. Some strains can cause genital warts, while others can increase the risk of certain cancers. Vaccination is available for some HPV strains.
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): This virus causes herpes, a lifelong infection with recurring outbreaks of blisters around the genitals or mouth (depending on the strain). There are 2 primary strains of this virus.
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus): The virus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). HIV weakens the immune system, making the body susceptible to other infections. While there is no cure, available medication can significantly manage HIV and allow people with HIV to live long and healthy lives.
Parasitic STDs
These are less common but can still be transmitted through sexual contact.
- Trichomoniasis: Caused by a parasite, this sexually transmitted disease (STD) can cause vaginal itching, burning, and discharge in women and sometimes discomfort in men.
- Pubic Lice (Crabs): These are small insects that attach to pubic hair and cause intense itching.
- Scabies: These tiny mites burrow into the skin, causing severe itching and a rash. While it primarily spreads through skin-to-skin contact, sexual contact can be a mode of transmission.
It’s important to note that this is not an exhaustive list, and other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) exist. Many women may not experience any symptoms, making regular STD testing even more crucial. Look out for these signs of STD in females and consider getting tested if you experience any of these signs. Remember, even if you don’t experience any symptoms, getting tested regularly is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Causes of STDs
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are caused by microscopic organisms that take advantage of sexual contact to spread from person to person.
Bacteria: These single-celled organisms multiply rapidly within the body, often infecting the moist tissues of the genitals, rectum, or mouth. During sexual contact, infected bodily fluids like semen, vaginal secretions, or even blood can come into contact with these areas, allowing the bacteria to enter a new host and establish itself.
Viruses: Even smaller and simpler than bacteria, viruses invade human cells and hijack their machinery to reproduce. During sexual activity, viruses can be transmitted through contact with infected skin or mucous membranes. This includes the genitals, rectum, and mouth. Some viruses, like HPV, can also be spread through skin-to-skin contact in the genital area.
Parasites: These single-celled organisms or small worms can also cause sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Trichomoniasis, caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis, is transmitted through vaginal fluids during sexual contact.
Transmission Modes
It’s important to remember that sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can be spread through various forms of sexual contact, not just vaginal intercourse.
- Vaginal Sex: This is the most common mode of STD transmission, as it allows for direct contact with infected bodily fluids.
- Anal Sex: This carries a high risk of STD transmission due to the fragility of the rectal lining.
- Oral Sex: While less risky than vaginal or anal sex, oral sex can still transmit STDs if there’s contact with infected genitals or sores.
Remember: Regardless of the type of sexual contact, practicing safe sex with barriers like condoms and dental dams can significantly reduce the risk of sexually transmitted disease (STD) transmission.
If you’re concerned about your sexual health or notice any potential signs of STD in females (like unusual discharge, pelvic pain, or burning urination), don’t hesitate to get tested. STD testing near me is a quick search away, and many clinics offer confidential and convenient options. Early detection and treatment of STDs are crucial to prevent complications and protect your health and the health of your partner(s).
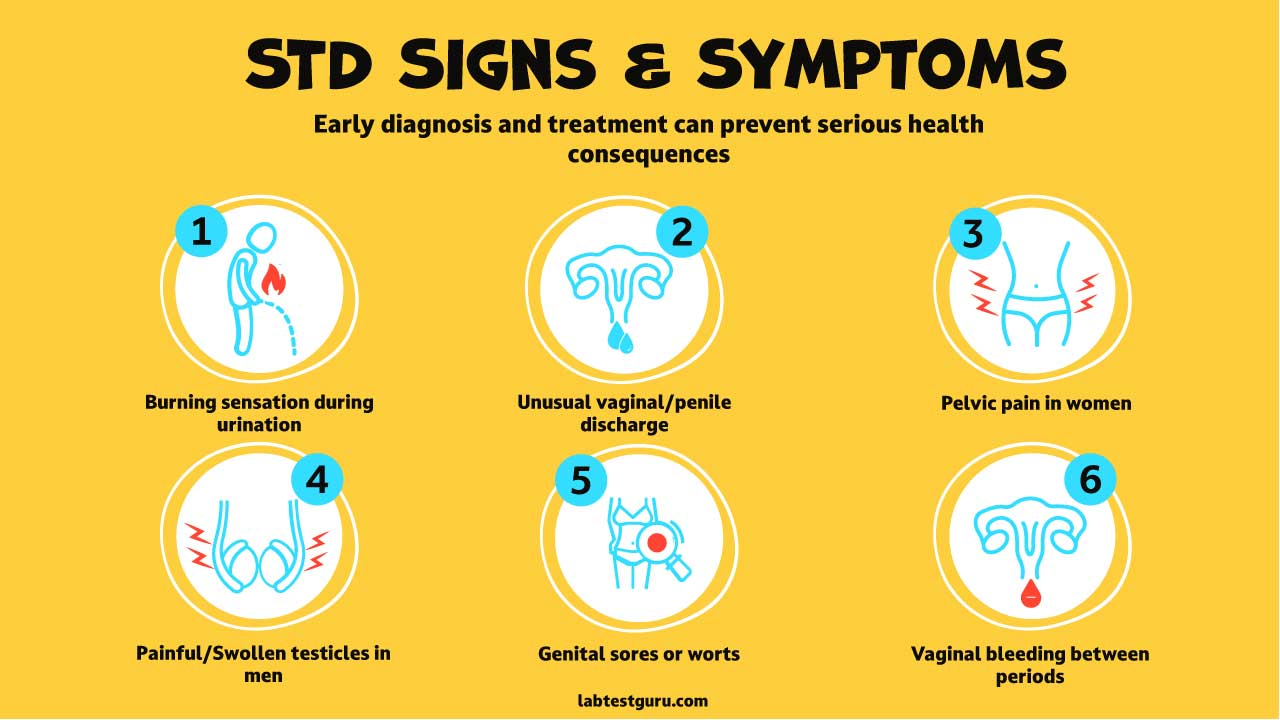
STD Signs and Symptoms
One of the biggest challenges with sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) is that many infections may not cause any symptoms initially, especially in the early stages. This can lead to a false sense of security and delayed diagnosis. This is particularly true for women, where some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) might not present any noticeable signs.
While symptoms can vary depending on the specific sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the infected area, here are some common ones to be aware of:
In both men and women
- Burning sensation during urination
- Unusual vaginal discharge or discharge from the penis
- Pelvic pain in women
- Painful or swollen testicles in men
Additionally, some STDs may cause
- Genital sores or warts
- Changes in skin color or texture around the genitals
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
However, it’s crucial to remember that the absence of symptoms doesn’t guarantee you’re STD-free. This is why getting tested regularly, even if you feel healthy, is essential. Early detection of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) allows for prompt treatment, preventing complications and protecting your partner(s) from potential infection.
Focusing on Women’s Health
While sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can affect anyone, some symptoms can be more noticeable in women. Here are some specific signs of STD in females to watch out for:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge that is thicker, discolored, or has a strong odor
- Pain or discomfort during sex
- Itching or burning around the vagina
- Bleeding between periods or after sex
If you experience any of these signs, don’t hesitate to see a doctor and consider getting tested. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent serious health consequences, like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and infertility.
Taking Charge of Your Health
Remember, knowledge is power. The more informed you are about sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and their potential signs, the better equipped you are to protect your health. STD testing near me is a simple internet search away, and many clinics offer confidential and convenient testing options. Taking control of your sexual health through regular testing is an essential step towards a healthy and fulfilling sex life.
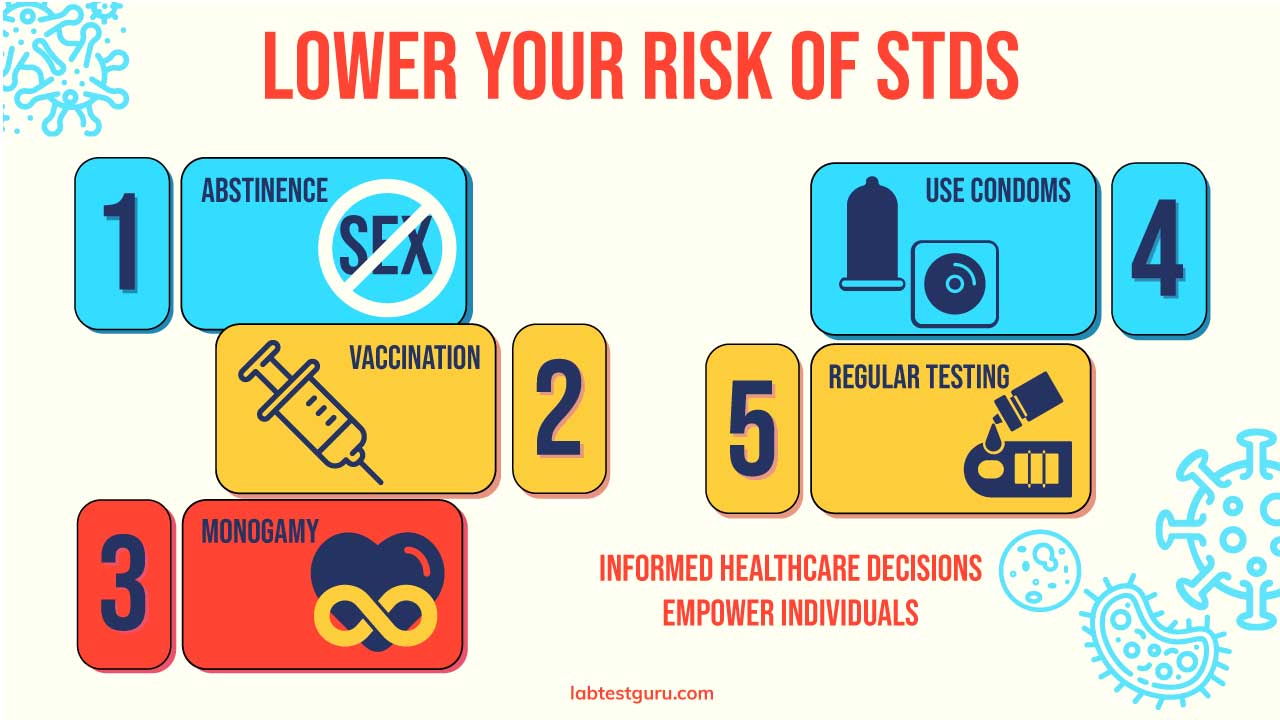
How to Prevent STDs?
Here are some of the most effective ways to lower your risk of contracting STDs.
- Abstinence: The most reliable way to prevent sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) is to abstain from sexual activity.
- Vaccination: Vaccines are available for some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as HPV and hepatitis B.
- Monogamy: Having a mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and is not infected can significantly reduce your risk.
- Condom Use: Consistently and correctly using latex condoms during all sexual activity provides a barrier against many sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
- Regular Testing: Regular STD testing, especially if you have multiple sexual partners or engage in risky sexual behaviors, is crucial.
Remember, open communication with your sexual partners about your sexual history and getting tested together is essential for reducing the risk of STDs.
Why Get Tested for STDs?
Early detection and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) offer significant benefits for both your personal health and the health of your partner(s).
Personal Health Advantages
- Prevent Complications: Left untreated, some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can lead to serious health problems. For example, Chlamydia and Gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women, which can increase the risk of infertility and ectopic pregnancy. Early detection and treatment can prevent these complications.
- Reduce Long-Term Health Risks: Some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), like HIV, can weaken the immune system and increase your susceptibility to other infections. Early treatment can help manage the virus and significantly improve your overall health. Other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), like HPV, can increase the risk of certain cancers if left untreated. Early detection allows for interventions that can prevent these complications.
- Improves Treatment Outcomes: Many sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are easily curable with antibiotics if caught early. Delaying treatment can make them more difficult to cure and potentially lead to antibiotic resistance.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing your sexually transmitted disease (STD) status can provide peace of mind and allow you to make informed decisions regarding your sexual health.
Protecting Your Partner(s)
- Prevent Transmission: By getting tested and treated for any sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) you may have, you significantly reduce the risk of transmitting them to your partner(s). This is crucial for maintaining healthy relationships and preventing the spread of infections.
- Promote Open Communication: Discussing sexually transmitted disease (STD) testing with your partner(s) fosters open communication about sexual health. This creates a safe space to address concerns and practice safe sex together.
Remember: Early detection is key! Don’t wait for symptoms to appear before getting tested. Signs of STD in females, while important to be aware of, may not always be present.
Potential Complications of Untreated STDs
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women
- Infertility in both men and women
- Increased risk of HIV transmission
- Chronic health problems
Protecting Yourself and Your Partner
By prioritizing STD testing and getting tested regularly, you’re taking a proactive step towards safeguarding your personal health and the health of your partner(s). It’s a win-win situation for everyone involved!
Choosing the Right STD Test
Deciding to get tested for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) is a responsible choice for your sexual health. But with various testing options available, choosing the right one can feel overwhelming.
At-Home STD Test Kits
Convenience and Privacy in Your Hands
At-home test kits offer a discreet and accessible way to get tested on your own terms. These kits typically come with everything you need:
- Sample collection materials: This may involve urine cups, swabs (vaginal, urethral, or oral) depending on the test.
- Clear instructions: The kit will provide detailed instructions on sample collection, packaging, and mailing.
- Prepaid return packaging: The kit usually includes a prepaid envelope or label to send your sample securely to a lab for analysis.
- Online results: Results are delivered electronically or by phone within a few days of the lab receiving your sample.
Pros
- Unmatched Convenience: Test on your own schedule, in the comfort and privacy of your own home.
- Discretion: Collect samples discreetly without needing a physical exam.
- Accessibility: Often readily available for purchase online or at pharmacies.
Cons
- Limited Test Options: At-home kits may not offer the same breadth of tests as a lab setting.
- Potential for Error: Improper sample collection can compromise the accuracy of the results.
- Less Certainty: Results might not be as definitive as a lab test, sometimes requiring confirmatory testing at a clinic.
Lab Testing
Expert Analysis for Definitive Results
Lab testing involves visiting a healthcare clinic or dedicated lab facility. A healthcare professional will collect the necessary samples, ensuring proper technique for accurate results. The types of samples collected can vary depending on the sexually transmitted disease (STD) being tested.
- Urine: A common sample for testing for Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and sometimes HIV.
- Swabs: These are used to collect cells from the genitals (vaginal, urethral, or oral) to test for various sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) like Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, HPV, and Herpes.
- Blood: Blood draws are used for specific tests like HIV and syphilis.
The collected samples are then analyzed in a certified laboratory with sophisticated equipment for accurate results. Results are typically available within a few days to a week and are delivered by the clinic or lab.
Pros
- Expert Touch: Trained professionals collect samples, minimizing the risk of user error and ensuring accurate results.
- Wider Test Range: Access to a broader variety of STD tests, including those not available in at-home kits.
- Confirmatory Testing: If needed, a lab setting allows for confirmatory testing to solidify positive results from at-home kits.
- Consultation and Treatment: Clinics offer guidance on interpreting results, discussing treatment options, and providing medication if necessary.
Cons
- Less Convenient: Requires scheduling an appointment and visiting a healthcare facility.
- Privacy Considerations: May involve a physical exam and interaction with healthcare professionals.
- Cost: Lab testing might be more expensive than at-home kits, although insurance may cover it.

Choosing Your STD Testing
Ultimately, the best option for you depends on your individual needs and preferences. Consider these factors:
- Convenience and privacy: Do you prioritize ease and discretion, or are you comfortable with a clinic visit?
- Type of test needed: Research the specific STD test you require and see if it’s available in at-home kits.
- Comfort level with sample collection: Are you comfortable collecting your own samples, or do you prefer a healthcare professional to do it?
- Budget: Consider the cost of the test kit or lab fees, and whether insurance coverage applies.
Remember, regardless of your choice, STD testing near me is a quick search away. Explore your options, get informed, and take control of your sexual health!
When to See a Doctor for STDs
While regular testing is crucial, there are situations where seeing a doctor for STD testing becomes even more important. Here’s when consulting a doctor is advisable:
- Experiencing Symptoms: As discussed earlier, many sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) don’t present symptoms, but some do. If you experience any concerning signs like burning urination, unusual discharge, genital sores, pelvic pain, or bleeding between periods, see a doctor immediately. They can perform a physical exam, order appropriate tests, and provide prompt treatment if needed.
- High-Risk Sexual Behavior: If you engage in sexual behaviors that increase your risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as having multiple partners or not using condoms consistently, consider scheduling regular testing with your doctor. They can advise on the most suitable testing frequency based on your individual risk factors.
Remember: Early detection and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are essential to prevent complications and protect your health and the health of your partner(s). Don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice if you have any concerns.
STD Treatment Options
The good news is that most sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) caused by bacteria are treatable with antibiotics. Effective treatment can eliminate the infection and prevent complications. Common bacterial sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) like Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis all respond well to antibiotic regimens prescribed by a doctor.
However, for viral sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) like HIV, HPV, and Herpes, there is currently no cure. These infections remain within the body for life. However, advancements in medicine offer ways to manage these viruses effectively. Medications can significantly reduce viral activity, lessen the frequency and severity of outbreaks, and even prevent transmission to partners in some cases.
The Key to Success: Completing Your Treatment
Regardless of the type of STD, it’s crucial to complete the full course of medication prescribed by your doctor, even if symptoms improve or disappear entirely. Stopping medication prematurely can lead to:
- Incomplete eradication of the infection: This can allow the bacteria or virus to become resistant to the medication, making future treatment more difficult.
- Increased risk of complications: Untreated infections can lead to serious health problems, like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or infertility.
- Potential for transmission to partners: Even if you don’t feel symptoms, incomplete treatment can still allow you to transmit the STD to your partner(s).
Taking charge of your treatment is essential for a full recovery and protecting yourself and your partners.
Conclusion
Getting tested for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) is a responsible step towards safeguarding your sexual health and the health of your partner(s). Now that you’re equipped with this knowledge, explore the resources available to learn more about specific STD tests and testing options that suit your needs. Remember, early detection and treatment are key to preventing complications.
Empowering you to make informed decisions about your sexual health is our priority.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health.
