What is Folate, and Why is It So Important?
Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is a powerhouse nutrient that plays a vital role in your body’s overall health. It helps with DNA production, cell growth, and brain function. But for certain groups—especially pregnant women—folate is absolutely essential. It helps prevent serious birth defects, supports fetal development, and ensures your baby gets the best start in life.
If you’re pregnant, trying to conceive, or belong to an at-risk group (such as people with absorption issues or those on certain medications), getting a folate blood test can help determine if you have adequate levels to support your health.
Quick Guide
Disclaimer: This information is based on research and is accurate to the best of our knowledge at the time of publication. Please note that the writer has not personally used or tested these products.
Why Pregnant Women Need Folate
Folate is crucial during pregnancy, especially in the early weeks when your baby’s brain and spinal cord are developing. Low folate levels can lead to neural tube defects (NTDs) such as:
- Spina Bifida: The spinal cord doesn’t form properly, leading to lifelong mobility issues.
- Anencephaly: A severe brain defect that is usually fatal.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Increased risk due to insufficient folate.
- Premature Birth & Low Birth Weight: Babies born with inadequate folate intake may face developmental issues.
This is why doctors strongly recommend folate supplements and monitoring through folate blood tests to ensure you’re getting enough.
Health Risks of Folate Deficiency in Growing Children
Folate deficiency doesn’t just affect pregnant women—it can also have serious consequences for growing children. Since folate plays a key role in brain development, cell production, and red blood cell formation, children who don’t get enough of this essential vitamin may face several health challenges.
- Developmental Delays: Lack of folate can slow cognitive, motor, and speech development, leading to difficulties in learning, coordination, and communication.
- Anemia: Without enough folate, the body struggles to produce healthy red blood cells, leading to fatigue, weakness, and a weakened immune system.
- Poor Concentration and Memory: Children with folate deficiency may have difficulty focusing in school, affecting their academic performance.
- Irritability and Mood Changes: Behavioral changes, increased fussiness, and difficulty managing emotions can be linked to low folate levels.
- Growth Issues: Folate is necessary for proper cell division, and a deficiency may result in stunted growth.
- Weakened Immune System: Children with inadequate folate levels may be more prone to infections and illnesses due to compromised immune function.
Ensuring children get enough folate through a balanced diet and, if necessary, supplements can help prevent these issues and support their overall well-being.
Signs You Might Have a Folate Deficiency
A lack of folate doesn’t just affect your baby—it can also impact your health. Common signs of deficiency include:
- Extreme fatigue
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Frequent headaches
- Irritability or mood changes
- Digestive issues like diarrhea
- Difficulty concentrating
Signs and Symptoms of Folate Deficiency in Growing Children
Folate deficiency in children can present with distinct and sometimes subtle symptoms. Because folate is critical for brain development and red blood cell formation, a deficiency may lead to:
- Delayed Cognitive Development: Children may struggle with memory, learning, and problem-solving skills.
- Slowed Motor Skills: Activities like crawling, walking, and hand-eye coordination may take longer to develop.
- Speech and Language Delays: Difficulty in forming words and sentences can be linked to insufficient folate.
- Persistent Irritability: Children may become unusually fussy, restless, or easily frustrated.
- Poor Appetite and Weight Loss: A deficiency can reduce hunger and overall energy levels.
- Frequent Infections: A weakened immune system due to inadequate folate can make children more susceptible to illnesses.
- Anemia: Low folate levels can lead to megaloblastic anemia, causing extreme fatigue, dizziness, and pale skin.
If a child shows any of these signs, testing for folate deficiency through a folate blood test and addressing it through diet or supplements can significantly improve their development and overall well-being.
Important Note: These signs can be subtle and may overlap with other conditions. If you suspect your child might have a folate deficiency, it’s crucial to consult with their pediatrician for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Who is Most at Risk for Folate Deficiency?
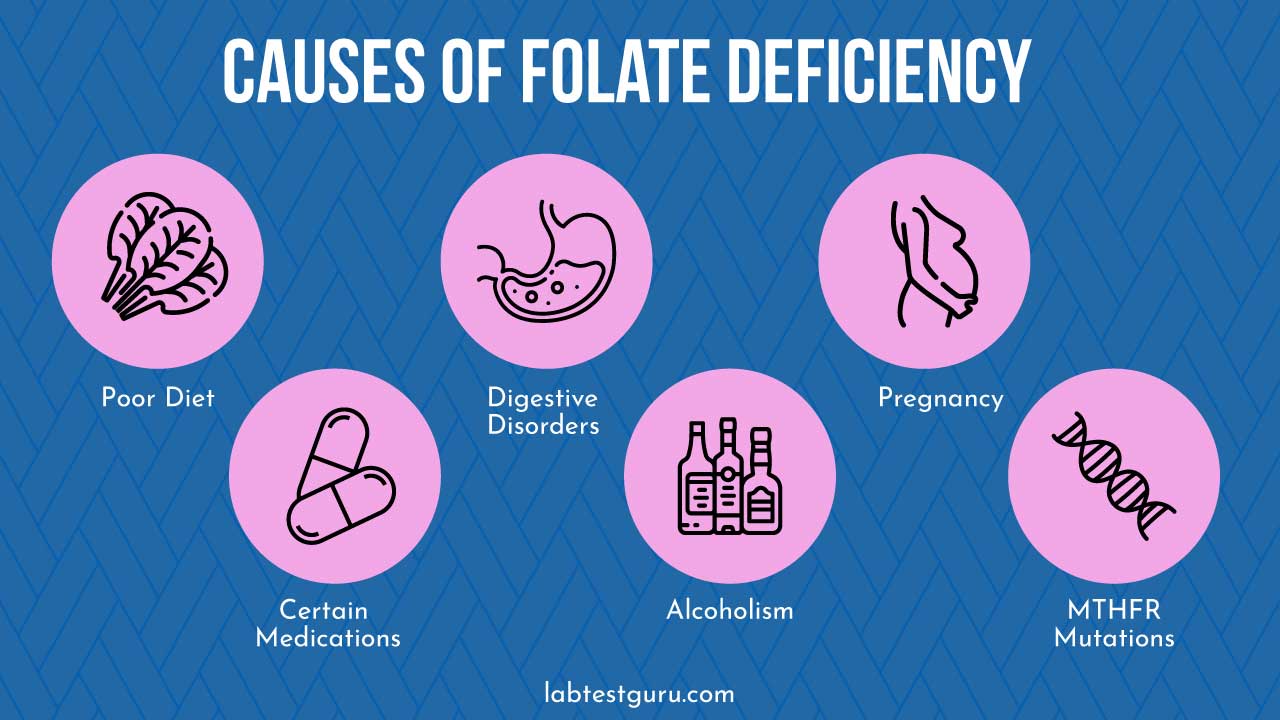
Certain individuals are more likely to have a folate deficiency. If you fall into any of these categories, you should consider getting a folate blood test.
- Pregnant or Trying to Conceive: Folate is crucial for fetal development.
- Individuals with Digestive Disorders: Conditions like celiac disease or Crohn’s can prevent your body from absorbing folate properly.
- Alcohol Consumers: Excessive alcohol can lower folate levels.
- People on Certain Medications: Some drugs, like methotrexate or anticonvulsants, interfere with folate absorption.
- Vegans and Vegetarians: Since animal products are a significant source of folate, plant-based eaters may need to monitor their levels.
How to Test for Folate Deficiency
A folate blood test is a simple way to check if your levels are sufficient. It can be done through:
- Lab-Based Blood Tests: You visit a lab where a healthcare professional draws blood from your vein.
- At-Home Testing Kits: Some brands offer finger-prick tests you can do from home, mailing your sample to a lab for results.
The reference range for folate can vary slightly between laboratories, but generally falls within:
Serum Folate:
- 2.7 to 17.0 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL)
- Or 6.12 to 38.52 nanomoles per liter (nmol/L)
Red Blood Cell (RBC) Folate:
- 140 to 628 ng/mL
- Or 317 to 1422 nmol/L
Recommended Tests
Personalabs Folate RBC Blood Test
- Tests for: Folate levels in your red blood cells
- How it works: Buy a lab test from Personalabs.com and schedule an appointment at your nearest local lab
- Specimen required: Blood from the veins
- Results in: 2 – 10 business days
- Special preparation: Do not take vitamin B9 or folate three to five days before the test. This test may also produce inaccurate results if the patient is taking high doses of biotin supplements (also known as vitamin B7, B8, vitamin H, or coenzyme R). Individuals are advised to stop taking biotin supplements for at least 72 hours prior to the blood draw.
About the test
This test measures the folate levels in your red blood cells (RBC-Folate), which provides a more reliable assessment of nutritional deficiencies than serum folate levels. Unlike serum folate, which can vary significantly due to recent dietary intake and absorption, RBC-Folate remains relatively stable, making it a more accurate indicator of long-term folate status. Measuring RBC-Folate is particularly important in diagnosing conditions such as severe alcoholism, malabsorption disorders affecting the small intestine, pregnancy, and different types of megaloblastic anemia.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✅ No doctor visit required ✅ Excellent service | ❌ Tests cannot be conducted at lab locations in Arizona, New Jersey, New York, or Rhode Island. |
Verisana B Vitamins Test (At-home test kit)
- Tests for: Folate and Vitamin B12 level
- How it works: Buy a kit from Amazon.com, collect your blood on a small card and mail it to a Verisana lab with a prepaid envelope
- Specimen required: Finger prick blood sample
- Results in: 7 – 10 business days
About the test
The Verisana Folate and B12 kit is an at-home test designed to measure the levels of these vital vitamins in your blood. Simply order your kit, collect a sample at your convenience, and send it back to the lab. Using advanced techniques like enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), the laboratory analyzes your sample to determine your folate and vitamin B12 levels. Your results will be accessible online and sent to you via email. The kit includes everything needed for testing—detailed instructions, sampling supplies, and a prepaid return shipping envelope. There are no extra costs; the price covers the scientific analysis and a comprehensive laboratory report.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✅ Easy-to-use ✅ Can be done at your convenience in the privacy of your own home ✅ CLIA-certified lab | ❌ Needs blood sample to dry for one hour and then shipped within 24 hours ❌ Due to regulatory reasons, this test is currently not available in NY/NJ/RI/MD ❌ Must be at least 18 & over to take the test |
Personalabs Vitamin B12 and Folate Test
- Tests for: Vitamin B12 and Folate levels in your blood
- How it works: Buy a lab test from Personalabs.com and schedule an appointment at your nearest local lab
- Specimen required: Blood from the veins
- Results in: 2 – 10 business days
- Special preparation: Dietary supplements containing biotin may interfere with this panel, causing results to be either falsely high or falsely low. We recommend pausing biotin-containing supplements 72 hours prior to being tested.
About the test
This test measures the vitamin B12 and folate level in your serum.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✅ No doctor visit required ✅ Excellent service ✅ HSA/FSA accepted | ❌ Tests cannot be conducted at lab locations in Arizona, New Jersey, New York, or Rhode Island. |
How to Boost Your Folate Levels Naturally

While supplements are often recommended, you can also increase your folate intake through diet. Some folate-rich foods include:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, romaine lettuce
- Legumes: Lentils, black beans, chickpeas
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges, lemons, grapefruits
- Fortified Foods: Many cereals and bread are enriched with folic acid
- Avocado & Nuts: Great plant-based sources
Treatment for Folate Deficiency
If your folate blood test shows low folate levels, don’t worry— folate deficiency is usually easy to treat! Your doctor may recommend:
- Daily Folate Supplements: Especially important for pregnant women.
- Dietary Adjustments: Increasing folate-rich foods.
- Treating Underlying Conditions: Addressing absorption issues if needed.
When to Consult a Doctor
If you’re planning a pregnancy, already pregnant, or experiencing symptoms of deficiency, speak with a healthcare professional. A folate blood test is a simple yet crucial step to ensure you and your baby stay healthy.
The Bottom Line
Folate is one of the most critical nutrients for pregnancy and overall health. A deficiency can lead to serious complications, but fortunately, it’s easy to detect through folate blood test and treat. If you’re in an at-risk group, getting tested can provide peace of mind and allow for early intervention if needed.
Whether through a lab test or an at-home kit, checking your folate levels through a folate blood test can be a small but vital step toward better health for you and your baby.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health.
References
- Zhao G, Ford ES, Li C, Greenlund KJ, Croft JB, Balluz LS. Use of folic acid and vitamin supplementation among adults with depression and anxiety: a cross-sectional, population-based survey. Nutr J. 2011 Sep 30;10:102. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-10-102. PMID: 21962075; PMCID: PMC3200167.
- Khan KM, Jialal I. Folic Acid Deficiency. [Updated 2023 Jun 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
- Viswanathan M, Urrutia RP, Hudson KN, Middleton JC, Kahwati LC. Folic Acid Supplementation to Prevent Neural Tube Defects: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2023 Aug 1;330(5):460-466. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.9864. PMID: 37526714.




